AI in Gaming
Artificial Intelligence can be utilised to overcome human limitations and has proven to be extremely beneficial. It has the potential to be applied productively and utilised for the betterment of society as a whole, from uses in medicine and engineering to targeted advertising and our everyday mobile apps. AI is the perfect marriage of creativity and technology, designed to complement and work with people, rather than in isolation. But, power and social advancement aside, where is AI used in entertainment? Video games, of course.

Artificial Intelligence is a wide-reaching branch of computer science emphasising the creation of intelligent machines that are capable of performing tasks which would usually require the input of human intelligence. It's an interdisciplinary science with multiple approaches but advancements in machine and deep learning are creating a paradigm shift in virtually every sector of the tech industry, revolutionising how video games are developed and played.
Many people have tried to imagine the scale of a future with AI and how far it could go, but so far, predictions are purely guesswork, with no clear answer to how this technology might grow or whether it may be evolving faster than humans. Ender's Game, the 1985 novel by Orson Scott Card, explores a military-grade simulation, anchored by an advanced, inscrutable Artificial Intelligence - the novel is set on Earth, at an unspecified point in the future of course, but spurs people to wonder how much longer these conceptual advancements in AI will be purely conceptual, raising questions about how far AI could in fact develop.
A brief history of AI in video games
Arcade games are one of the earliest instances of commercial gaming using stored patterns to simulate arbitrary enemy movement. Space Invaders, 1978, was one of the first games to make use of this and kickstarted the evolution of AI in gaming. In 1980, Pac-Man also hit the arcades, bring AI into a complex maze game, allowing the colourful characters involved to exhibit different personality traits. A few decades passed, and The Sims arrived on the scene in 2000, where the heavy reliance on AI allowed the player to assume the role of an omnipotent being from the comfort of their own home, able to watch their characters live their own independent lives with minimal required input.
Further development lead to Artificial Intelligence being able to generate responsive, adaptive or intelligent behaviours, primarily in Non-Player Characters that were designed to function and react like humans. These NPCs were now able to hunt players, building on the generic attack/defence modes seen in the earlier arcade style games. They also gained the ability to create audible and physical disturbances to the environment around the player, allowing for a more immersive experience with open-world gaming - all features present in stealth games like Metal Gear Solid, which saw advancements like these as early as 2002. But AI was still very rough around the edges, and that was the case for a few more years to follow.
Fast-forward to the last decade, and online gaming dominates the market, largely due to gamers wanting opponents with impulsive, erratic, unpredictable behaviour - opponents who feel real, human. This high demand for a more authentic and human experience in games meant that single-player game developers had to up their game, enhancing open-world environments to keep up and continue to improve non-player characters which could one day rival human players. And all through ever-evolving AI.
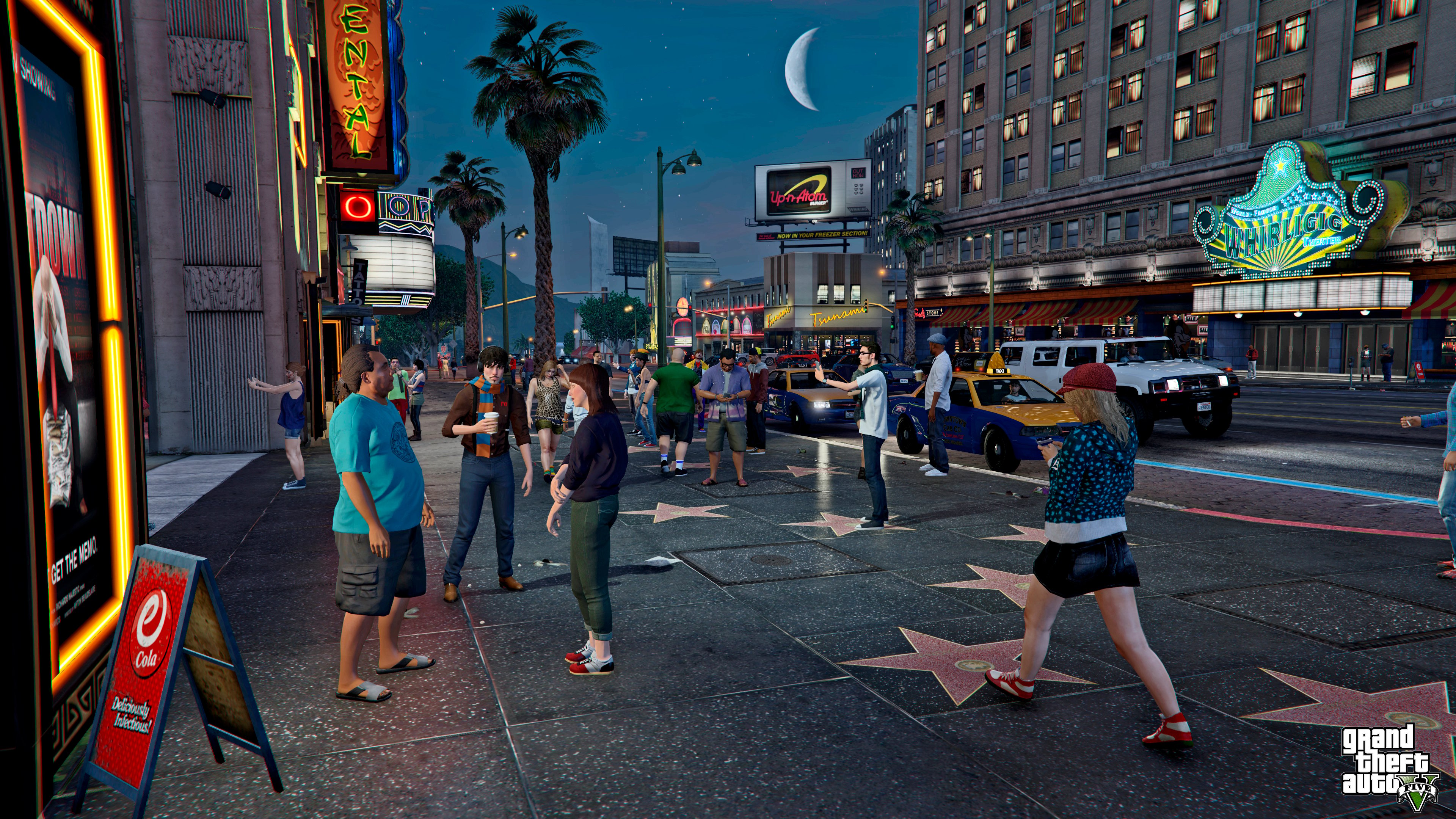

In 2013, for example, Rockstar's GTA:V pushed the open world genre to the next level, flaunting some of the most responsive and numerous NPCs seen in gaming. Hitman Absolution managed to do something very similar only the year before and in some cases, those NPCs were probably a little smarter. But GTA:V's defining feature was the scale of it all; seemingly thousands of individual NPCs going about their business in the beautiful Los Santos, existing in their day-to-day lives regardless of player presence, with their reactions to the player, and all the inevitable destruction, designed to be as realistic as possible. Not long after that, numerous other games joined them, but still none could quite offer players the same challenge as their online, human counterparts...
But now, Big Data in gaming is capturing information on how we game like never before, tracking data points, patterns and trends, allowing developers to tailor gaming experiences to individuals. Professor Arend Hintze, for example, recently created an AI that adapts to the player's behaviour, matching their ability. And there are other applications for AI too, outside of NPC implementation - take the AI used in conjuction with Bing Maps, to aid in generating 3D models for the entire world, in Microsoft's Flight Simulator 2020.
AI is able to work extremely well alongside data analytics and is the primary reason why AI and Big Data are now seemingly inseparable. But many video game developers are hesitant to build advanced AI into their games, for fear of losing control over the overall player experience. In fact, the goal of Artificial Intelligence in video games is arguably not to create an unbeatable entity for players to struggle against for all eternity, but to maximise player participation and enjoyment over long periods of time. This hesitance doesn't mean that there is no space for Artificial Intelligence in the future gaming industry, with a wealth of evidence to prove otherwise, but the future of AI in gaming is a much-debated subject. Whatever the outcome though, the gaming industry will continue to evolve rapidly, and AI and Big Data are set to lead the industry into new, uncharted territories.
Comments
Post a Comment